Two reports by the University of Cyprus show the Cypriot economy in decline and the uncertain growth trend for 2020 with the main retardant being the coronavirus-imposed lockdown in March and its impact.
The university’s Economics Research Centre said in its outlook for the rest of the year that “as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, real economic activity in Cyprus is projected to contract sharply in 2020, (while) real GDP growth in 2020 is projected at -7.5%.”
This is a downward revision by 0.6 percentage points compared to the projection in May.
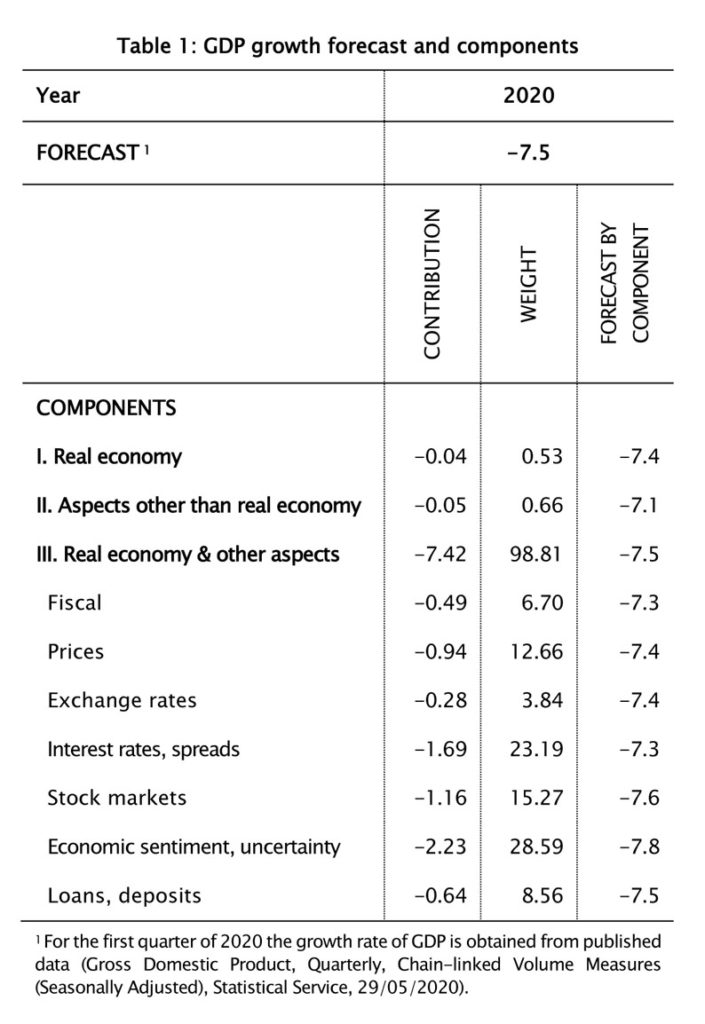
The ERC growth forecast is close to the projections published by the Central Bank of Cyprus (-7.3%) and the European Commission (-7.7%).
“The growth forecast incorporates the unprecedented negative developments in many indicators over the March-June period, as well as the effects of a negative shock to external demand for tourist services due to the pandemic; the shock is assumed to impact several branches of the economy for the rest of 2020.”
The negative outlook for 2020 is mainly driven by the sudden slowdown in domestic activity and the output contraction in Europe in the first quarter of the year, the collapse of economic sentiment in Cyprus and the EU, as well as the adverse performance of financial markets and heightened market volatility in the previous months, the ERC outlook said.
“Nonetheless, there are some factors that are expected to mitigate the downturn. These include the increased government expenditure to alleviate the effects of the pandemic; the recent declines in international oil prices and the absence of upward price pressures that back real incomes; and the low levels of domestic and European interest rates.”
CPI inflation is projected to fall to -0.7% from 0.3% in 2019, “driven by the recent sharp declines in international oil prices and weak demand due to the COVID-19 pandemic”.
Uncertainty remains
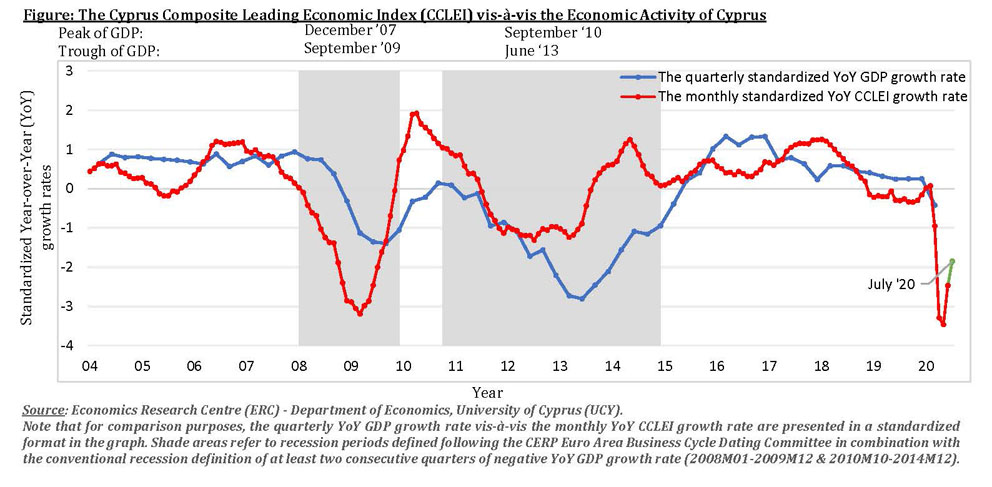
Meanwhile, the Cyprus Composite Leading Economic Index (CCLEI) compiled by the ERC and the Hellenic Bank research unit, recorded a decrease of 8.5% (from year to year) in June reaching a level of 99.6, after year-over-year reductions of 11.3% in May and 10.6% in April.
“The negative year-over-year growth rate of the CCLEI in June reflects the uncertain environment caused by the pandemic and its effects,” said the report.
The authors of the CCLEI said tourism has been significantly affected by the restrictive measures taken by the Cypriot government as well as other countries, with tourist arrivals in June and July being considerably lower compared to the corresponding months last year.
In contrast, the report said that the drop of the Index is restrained mainly by a number of domestic variables that record significant improvement in June and July compared to previous months.
“Although preliminary estimates indicate negative year-over-year growth rates for the volume of retail sales and electricity production in June and July as well as for the total number of sales contracts in July, these year-over-year reductions are much smaller than the year-over-year reductions recorded in previous months.
“Moreover, the improvement of the Economic Sentiment Indicator (ESI) in the euro area, including Cyprus, combined with the fact that the value of visa card transactions continues to increase, reflects the gradual improvement of the economy as well as the transition to electronic methods of payment as a precautionary measure against the coronavirus pandemic. “
The report concluded: “The reversal of the downward trend of the CCLEI for June as well as of the flash estimate of the Index for July indicates some improvement in economic activity.
The outlook of economic activity in Cyprus is subject to extremely high uncertainty due to the unpredictable development of the pandemic and its consequences.”
The CCLEI Index is designed to provide early warning signals for the turning points of business cycles i.e., early evidence of the turns in economic activity.
This index comprises leading economic activity variables which tend to lead to changes in the overall economic activity.
The components of the index include local and international leading indicators such as the Brent Crude oil price, the euro area Economic Sentiment Indicator (ESI), the total sales of contracts, tourist arrivals, the value of electronic card transactions, the retail trade sales turnover volume index, and the volume index of electricity production.