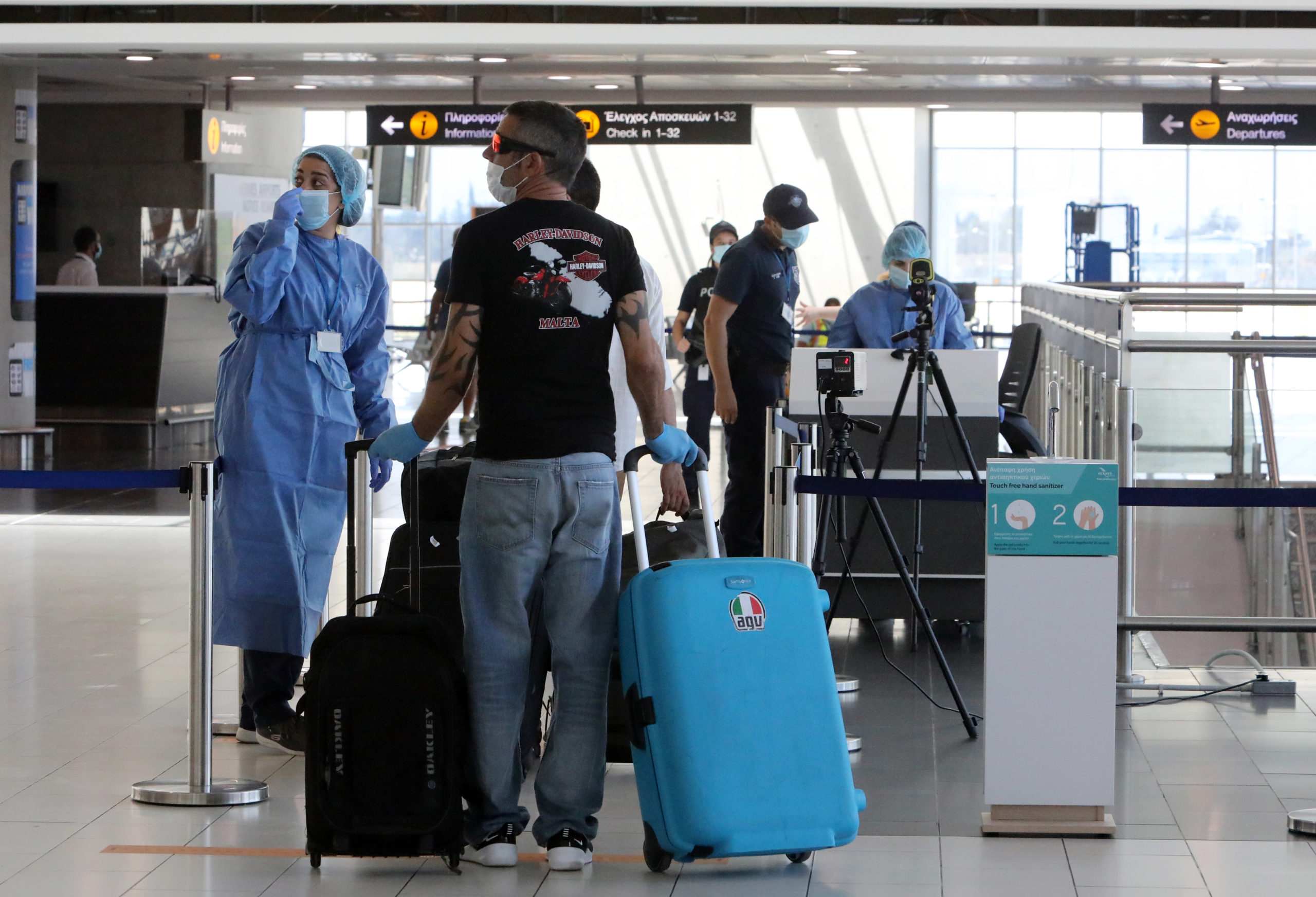
From 1 August, Cyprus will be adding the UK to its ‘safe’ list but will not allow entry to visitors from Bulgaria or Algeria after health authorities revised their COVID-19 risk.
These two countries have dropped off category B due to their worsening coronavirus data while Georgia was upgraded from Category B to A.
Cyprus will be welcoming back UK tourists from 1 August, Cyprus’ biggest travel market, after placing the country on the safe entry list but in the secondary band where visitors need to provide a negative COVID-19 test.
The Health Ministry announced the UK has been placed in category B, a higher risk band of countries than those that do not need a test like Germany and Greece.
Regarding Bulgaria’s demotion, which came after a spike in cases found to be positive for coronavirus after arrivals carried proof they had tested negative before arriving in Cyprus.
Bulgaria’s epidemiological data has also worsened as daily cases more than doubled from the beginning of the month.
The country’s health authorities are now reporting around between 200 and 300 cases a day, 330 last Wednesday.
Algeria has seen a resurgence in cases going from around 200 a day at the beginning of July to reporting 675 on 24 July.
In revaluating its travel list, the ministry said the update took into account the recommendation of the European Council dated June 30 for the gradual and coordinated lifting of travel bans to the EU.
That recommendation set back Cypriot tourism sector hopes of saving the season as it saw Israel removed from Category B to a higher risk country where there are no regular flights to Cyprus.
Anyone coming from a Category C country is required to self-isolate for 14 days.
Visitors from the 23 classified Category A countries are not required to provide a negative COVID-19 test.
Arrivals from countries in Category B need proof they have tested negative for COVID-19 within 72 hours prior to boarding their flight to Cyprus.
All passengers, irrespective of category, are obligated to submit an application online for CyprusFlightPass (https://cyprusflightpass.gov.cy/) within 24 hours of departure.
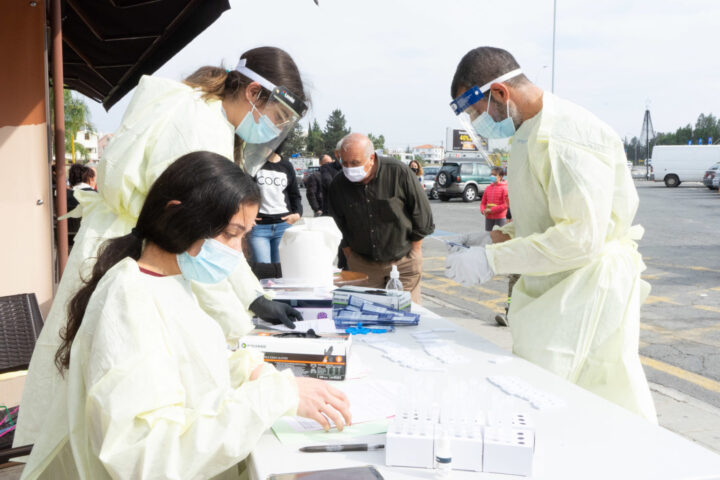
For public health reasons and to monitor the epidemiological situation, passenger arrivals are randomly tested.
Classification of countries is based on their reproduction rate R (t) for COVID-19, the number of new cases, the number of tests, the mortality rate per 100,000 people, the estimated prevalence and WHO indicators.
The ministry says classification of countries based on epidemiological risk is “exceptionally dynamic” and can change at any given moment as the pandemic develops.
Group A – Low-risk countries
These are countries with R (t) of below 1 and/or a small number of new cases (<1/100,000 inhabitants a day) and/or very low COVID19 mortality (<5-10/100,000 inhabitants) and/or sporadic cases or cluster of cases according to WHO and /or at least satisfactory tests (>3000 tests/100,000 residents):
EU members: 1) Austria, 2) Germany, 3) Denmark, 4) Greece, 5) Estonia, 6) Ireland, 7) Latvia, 8) Lithuania, 9) Malta, 10) Hungary, 11) Poland, 12) Slovakia, 13) Slovenia, 14) Finland
Members of Schengen: 1) Switzerland, 2) Iceland, 3) Liechtenstein, 4) Norway
Third countries: 1) Georgia, 2) Japan, 3) Canada, 4) New Zealand, 5) South Korea
Group B
These are countries with R (t) above 1 and/or new cases of >1/100,000 people a day and/or increased COVID-19 mortality (>10/100,000 people) and/or limited lab tests (<2000 tests/100,000 people) or lack of classification by WHO.
The Category now includes 19 countries down from 21 in the previous list.
EU members: 1) Belgium, 2) France, 3) Spain, 4) Italy, 5) Croatia, 6) The Netherlands 7) the Czech Republic
Small nations: 1) Andorra, 2) Monaco, 3) Vatican City, 4) San Marino
Third countries: 1) Australia, 2) Morocco, 3) Ruanda, 4) Thailand, 5) Tunisia, 6) Uruguay, 7) China